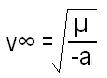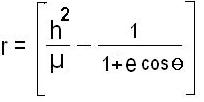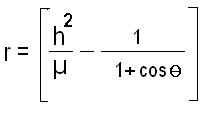What is the formula Kepler’s equation for calculating orbits?
In orbital mechanics, Kepler’s equation relates various geometric properties of the orbit of a body subject to a central force.
The formula Kepler’s equation for calculating orbits is given as,
M = E – ϵ sin E
M = the mean anomaly
E = the eccentric anomaly
ϵ = the eccentricity
It is a transcendental equation because sine is a transcendental function. It means that it cannot be solved for E algebraically. Numerical analysis and series expansions are generally required to evaluate E.