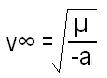What is the equation or formula for Bohr model for third postulate ?
An electron jumps from orbit of higher energy to an orbit of lower energy which radiates energy in form of photons. The energy emitted is equal to difference in the energies from the two orbits.
The equation or formula for Bohr model for third postulate is given as,
hv = En – Ep
ΔE= En – Ep
ΔE = difference in energies of higher orbit and lower orbit.
En = energies of nth higher orbit and Ep =energies of pth lower orbit
h = Planck’s constant
v = frequency of radiation emitted or absorbed